Industrial Networks EVOLVED
Easily connect Trout hardware to your network, and leverage its "DMZ in a box" features, to secure connectivity, simplify data flows and automate compliance controls.
Physical Device
Overlay Network Topology
Simple UI
Layer 7 Decryption
Automated Compliance Controls
Industrial MQTT/HTTP Proxy
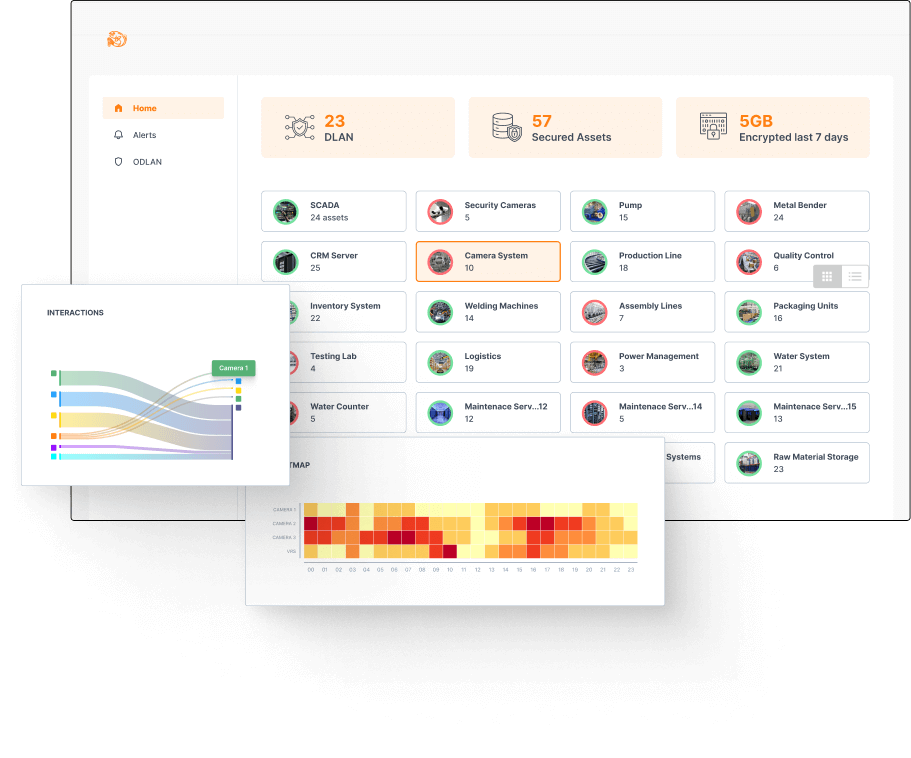
Demilitarized LAN (DLAN) Difference
Demilitarized LAN creates virtualized DMZs over existing physical networks, enhancing security by isolating critical assets into micro segments to prevent lateral threats.
TROUT FEATURES
Implementing a Zero Trust Approach Using DLAN
BENEFITS
Why Choose Trout CyberSwitch?
Simple Hardware Installation
Add Trout CyberSwitch to your network by connecting it to your existing switches.
- Simple to install
- On-premise data processing
- Extend your current systems

.png?width=564&height=636&name=Group%20265%20(1).png)
User-friendly UI
Structure your network to enforce zero-trust access management via a simple GUI.
- Create a secure network overlay with click-buttons
- Enforce Access-Control, at the protocol level
- Built-in end-to-end authentication and encryption
- Get full log visibility through built-in proxies
- All accessible via an intuitive UI
User-friendly UI
Structure your network to enforce zero-trust access management via a simple GUI.
- Create a secure network overlay with click-buttons
- Deploy the built-in DNS proxy
- Built-in end to-end authentication and encryption
- All accessible via an intuitive UI
.png?width=564&height=636&name=Group%20265%20(1).png)
Accelerate Innovation and Compliance
Quickly deploy new technology in your floor and accelerate compliance efforts.
- Built-in routing and virtual IP resolution
- Securely expose data through the Demilitarized LAN architecture
- Access control and log collection
- Compliance automation for Access Control, Identification and Authentication, and System and Communications Protection

"Trout offers a highly unique product that provides immediate resolution to a number of key OT issues. The introduction of a piece of hardware that can segment, troubleshoot, and provide intelligence about OT operations is truly groundbreaking. "
“It offers unique security capabilities, particularly in terms of applied security and operating at a layer 7 level. This sets it apart from other tools in the OT security space that primarily focus on vulnerability management.”
“Their hardware-based approach to network segmentation and security can address our unique needs, across our entire environment.”
“We were impressed by the simplicity to deploy and our ability to see more in a few days.”
"It's a universal problem, and I think they've got an idea of how to fix it. Feeding logs into my SIM and existing security operations is super clever."
Easily accelerate and secure your industrial sites
At Trout, we work to help our customers deliver agile and secure networks, and to be able to tackle their digitalization efforts, from a strength position
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a DMZ?
A DMZ, or Demilitarized Zone, in the context of network security, refers to a physical or logical subnetwork that separates an internal local area network (LAN) from other untrusted networks. In today’s environments, IT or Office VLANs require constant access with Internet services - for SAAS, video calls, etc - and DMZ should be implemented between these network segments and critical OT ones.
What is the difference between a VLAN and a DMZ?
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) and a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) serve different purposes in network design. A VLAN is used to segment a physical network into multiple, isolated logical networks. This segmentation is usually done for managing broadcast traffic, applying policies, or separating different types of traffic for security or organizational reasons. On the other hand, a DMZ is specifically used to improve security by isolating external-facing services from the internal network.
Which frameworks and organizations recommend a DMZ?
Several cybersecurity frameworks and organizations recommend the use of DMZs as part of a layered security strategy. Notable among these are:
- ISO/IEC 27001: This international standard for information security management systems (ISMS) recommends implementing network segmentation and segregation, which include DMZs, to protect sensitive data.
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology): NIST's cybersecurity guidelines often include the use of DMZs to protect internal networks from untrusted external networks.
- IEC 62443: IEC 62443, the leading international standard for security in automation environments, recommends to shield OT systems with a DMZ with front and back firewalls.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): For organizations that handle credit card information, PCI DSS requires the implementation of DMZs to separate payment systems from other network resources.
- ANSSI (National Agency for the Security of Information Systems in France): ANSSI provides recommendations for network segmentation and the use of DMZs to secure critical infrastructure.
What functionalities should a DMZ have?
A well-configured DMZ should provide the following functionalities:
- Service Isolation: The DMZ should host only the services that need to be accessible from the untrusted network, minimizing the risk of internal network exposure.
- Access Control: It should strictly control incoming and outgoing traffic between the DMZ, the internal network, and the internet using firewalls and other security appliances to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitoring and Logging: The DMZ should be equipped with tools to monitor and log activities, allowing for the detection of suspicious behavior and potential breaches.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) within the DMZ to identify and block malicious activities.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Services hosted in the DMZ should be regularly updated and patched to protect against known vulnerabilities.
The Trout Cyberbox simplifies the implementation of these DMZ functionalities by providing a hardware solution that automates the setup and management of a secure IDMZ environment, adhering to recommended security practices and standards.
.png?width=50&height=50&name=Vector%20(1).png)
.png?width=56&height=50&name=Vector%20(3).png)


.png?width=63&height=63&name=Frame%20614%20(1).png)
.png?width=63&height=63&name=Frame%20614%20(2).png)